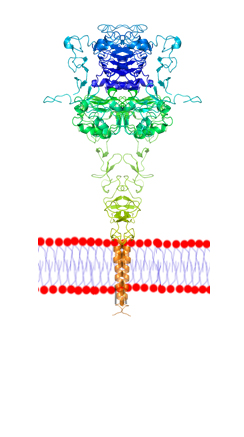
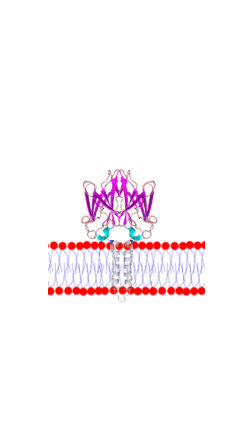
Ciloa has developed the sole technology to produce all types of complex membrane proteins on exosomes. This allows to work with the families of membrane proteins that are called “undruggable”, but that are also the most promising therapeutic targets. Of these are the GPCRs (G-protein coupled receptors), and the ion channels .
OVERCOME UNDRUGGABLE MEMBRANE PROTEINS
MAIN TARGETS OF CURRENT AND FUTURE DRUGS
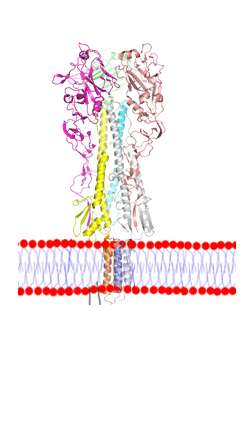
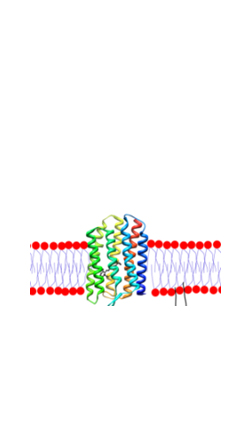
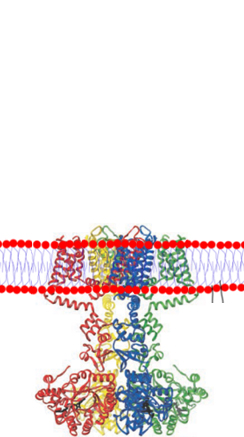
Ciloa produces native transmembrane proteins, such as receptors (GPCR, Receptor Kinases), ion channels, transporters, viral envelope proteins. These proteins may have one or several transmembrane domains and can be produced as monomers, homo-oligomers or hetero-oligomers.
Membrane proteins are responsible for these vital connections between the internal and external environments. Because of their strategic location they are the main targets of current and future drugs used in prevention and therapies.
Membrane proteins may have a single-transmembrane domain or multi-transmembrane domains. Due to their high hydrophobicity, multi-transmembrane proteins are the most difficult to produce out of cells.
Due to their crucial physiological functions, the most promising therapeutic targets are the receptors that belong to the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR), receptor kinase and ion channel classes.